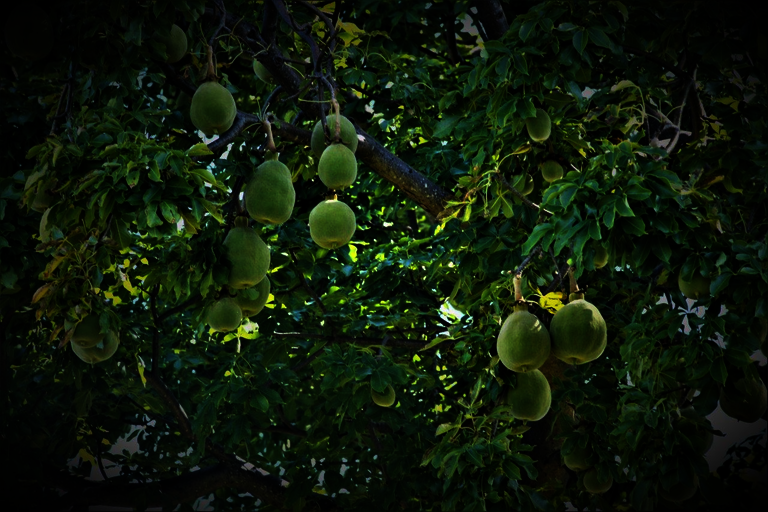
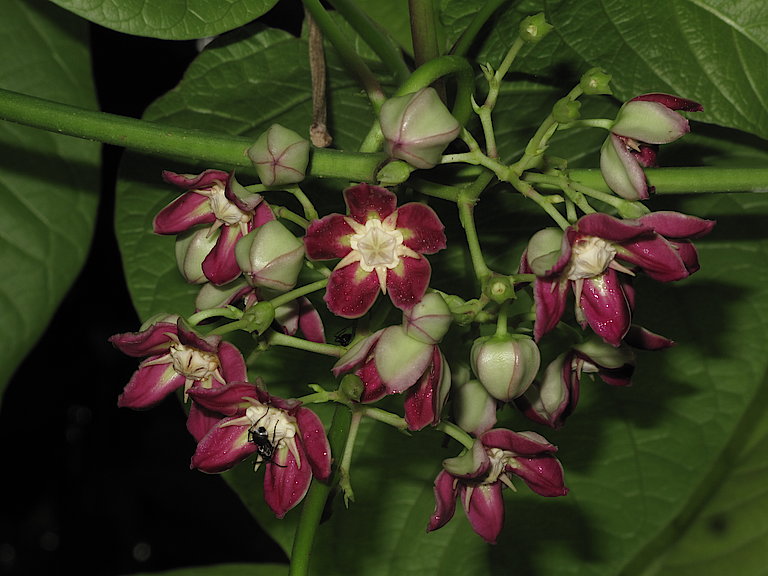
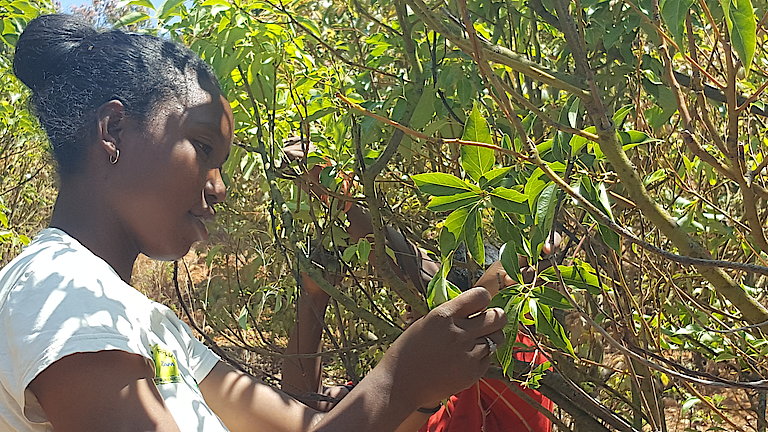
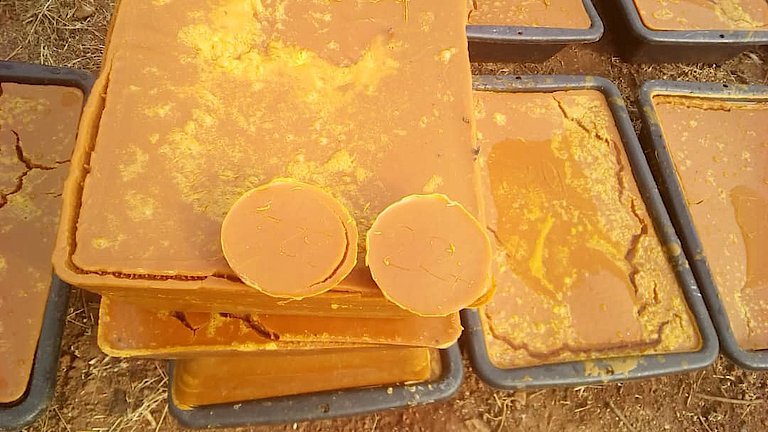
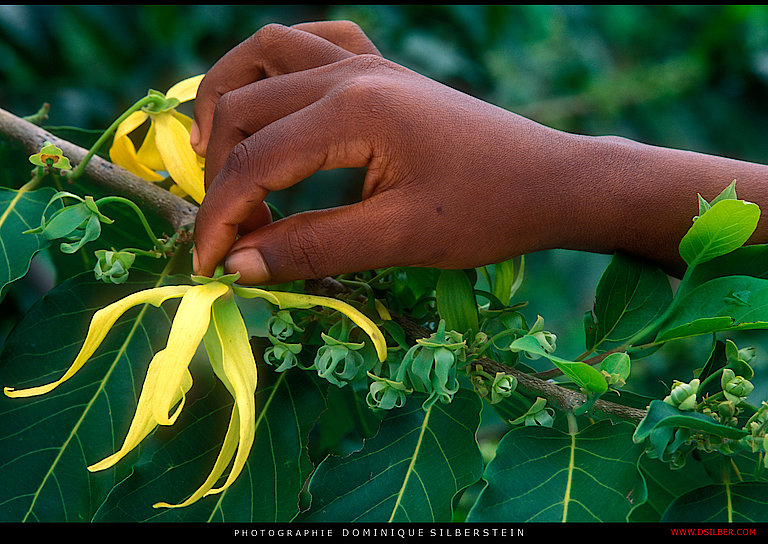
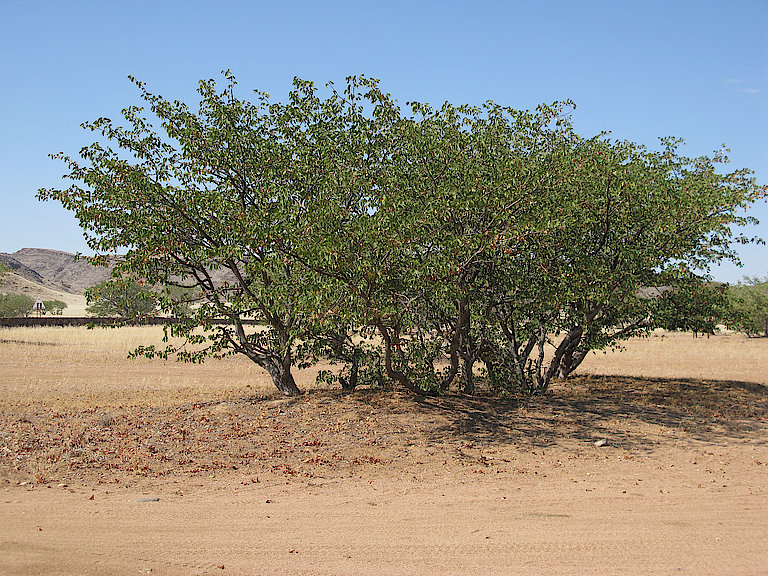
Marula is a fruit-bearing tree abundant in many parts of southern Africa and with ecological, economic and social significance. It is perennial and drought-resistant and produces an abundant crop. It survives for up to 150 years, so Marula’s commercial development could be key to future climate change mitigation strategies. The yellow fruit is traditionally used to make beer and juices, and is being explored for its flavour, fragrance and health potential in international food and beverage markets. Marula oil is pressed from the kernel for export to cosmetics producers. The Marula sector in southern Africa has potential to expand production and enter new export markets, stimulate rural development and create jobs.
Sustainable Use
Marula is classified as least concern status and not listed on CITES. As demand increases, harvesters are being trained in best practice and cultivation and production protocols developed.
Challenges and opportunities
The supply of Marula fruit exceeds demand, so suppliers and producers have little price leverage. Other challenges include the cost of organic and fair-trade certification, and compliance testing and certification. Access to new markets requires producers to satisfy international regulators concerned with consumer food safety, evidence of clean and hygienic manufacturing, and local standards and testing procedures. Marula has a very strong history of safe use, but this needs to be formally documented to comply with international regulations.
Development of the Marula sector
The development of a successful Marula economy requires a coordinated approach, collaborative planning, shared objectives, development and implementation of quality standards and strategies to access growing markets. The sector includes all people and organisations in the value chain, from harvester communities and cooperatives to product developers, exporters and consumer product manufacturers and marketers. It includes traditional knowledge holders, government, trade associations, regulators, research institutions, investors and funders. The sector must take account of differing national ABS regulations, ensure conservation and sustainable use, and will require evidence-based ecological, economic and social baseline data and monitoring. Full commercialisation of Marula will require improved genetic selection, domestication and cultivation, improved quality and reliability; as well as sustainable harvesting from the natural resource base. Biodiversity conservation and sustainable use will require capacity development, training and funding to protect and develop the resource for future generations. The sector needs to develop a scientific basis for claimed Marula benefits which can be articulated at industry, consumer and policy level. The sector should remain under the control of people and organisations in Southern Africa where the natural resource exists.
The current goal of the sector is to open the EU market for ingredients and products derived from Marula fruit, by addressing the EU Novel Foods Regulation [EU 2015/2283]. The sector sees scope for significantly increased Marula oil exports from the SADC region, and a 10% increase in employment in the sector within two years. Sustainable management of the resource is recognised as critical as the sector grows, and resource assessments have been conducted in two countries with an assessment being planned for SA. The aim is for a 20% increase in sustainably managed and utilised Marula growing areas. A GQSP-SA standards and quality training syllabus is being rolled out. Work is underway to improve Marula producers’ compliance with Access and Benefit-sharing requirements, in consultation with DFFE. The sector is consolidating published scientific data and traditional knowledge on the benefits of Marula oil, and looking at providing evidence for claims about its health benefits and efficacy in cosmetics and dermatology. Longer-term aims include securing Geographical Indicator status or other IP protection for Marula from southern Africa, funding for research, and formal analysis of the potential market.
Further links and information
Watch the French version of the video here.
Further information about the Marula sector
Cyril Lombard: cyril(at)biotradeventures.com